

("Constructor: " + web) Ĭop圜onstructor obj1 =new Cop圜onstructor ("Example of Copy Constructor in Java")

Example to Understand Copy Constructor in Java: package Demo Output: This is a no-argument constructor Copy Constructor in Java:Ī copy constructor is used for copying the values of one object to another object. Sample Program for Default Constructor: package Demo If you do define a constructor for your class, then the Java compiler will not insert the default no-argument constructor into your class. Once the class is compiled it will always at least have a no-argument constructor.
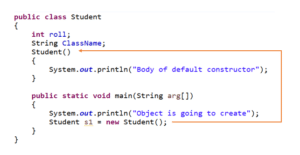
Therefore, it is also known as a no-args constructor. If we don’t define a constructor in a class, then the compiler creates a default constructor(with no arguments) for the class. Output: Student Name: Ashok and Student Id: 101 Default Constructor in Java:Ī constructor that has no parameter is known as the default constructor. ("Student Name: " + student1.name +" and Student Id: " + student1.id) Student student1 = new Student ("Ashok", 101) This would invoke the parameterized constructor. with the values of passed arguments while constructor would initialize data members Example to Understand Parameterized Constructor in Java: package Demo If we want to initialize fields of the class with our own values, then use a parameterized constructor. Types of Constructors in Java:īasically, there are three types of constructors in java:Ĭonstructors with parameters that can be used to initialize the internal state (fields) of the newly created object are known as Parameterized Constructors. Access modifiers can be used in constructor declaration to control its access i.e which other class can call the constructor.A constructor in Java cannot be abstract, final, static, and Synchronized.If you don’t write a constructor for your class, the compiler will give a default constructor. Every class should have at least one constructor.If you keep the return type for the constructor, it will be treated as a method. Constructors must not have a return type.The name of the constructor must be the same as that of the class name in which it resides.You can distinguish constructors from other methods of a class because constructors always have the same name as the class. They might also do other things necessary to make the object usable. Why do we need a Constructor?Ĭonstructors initialize the new object, that is, they set the startup property values for the object. Each time an object is created using the new keyword at least one constructor (it could be the default constructor) is invoked to assign initial values to the data members of the same class. The new keyword here creates the object of class M圜lass and invokes the constructor to initialize this newly created object. When we create the object of M圜lass like this: Let’s say we have a class M圜lass in the above declaration. This is a simple Java Constructor Declaration example: Constructors have no return type, not even void. Once defined, the constructor is called automatically immediately after the object is created, before the new operator completes it. It has the same name as the class in which it resides and is syntactically similar to a method.
#Java this constructor code#
The constructor is a block of code that initializes the newly created object.Ī constructor initializes an object immediately upon creation. This automatic initialization is known as Constructors. Java allows the object to initialize itself when it is created. At the end of this article, you will understand what are Constructors and their type as well as their role and responsibility in Java Applications with Examples. Please read our previous article, where we discussed Classes and Objects in Java. In this article, I am going to discuss Constructors in Java with Examples. Data Structures and Algorithms Tutorialsīack to: Java Tutorials For Beginners and Professionals Constructors in Java with Examples.Looking to learn Java programming in an online class environment? Check out our guide to the Best Online Courses to Learn Java. In this programming tutorial, we will learn about the concept of classes and objects in Java with the help of many code examples. Once defined, we can create many similar objects using the same class. So, before we create an object, we first need to define the class. So what does all this have to do with classes? A Java class is like an object constructor, or a “blueprint” for creating objects. All Java objects possess attributes, such as weight and color, and methods, such as drive, brake, and even knit. For example, a car is an object, as is your Grandmother (sorry grandma). As such it represents real world entities – both living and inanimate – as objects. Java is an Object-Oriented (OO) language.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
